Deviation Management System & Continuous Improvement
The SoluDyne Deviation System automates the deviation management processes, eliminates manual paperwork and reduces the time required to document, investigate and resolve deviations.
The SoluDyne Deviation System contributes to improving quality, reducing risk and facilitating compliance with regulations, as well as increasing learning in the organization.
The Deviation Management System is based on ISO and provides a centralized platform for capturing and analyzing deviation data, enabling effective collaboration and ensuring comprehensive compliance.
Includes standard reporting templates within all deviation categories with the possibility for Customer to modify existing or create forms and workflows in one flexible solution.
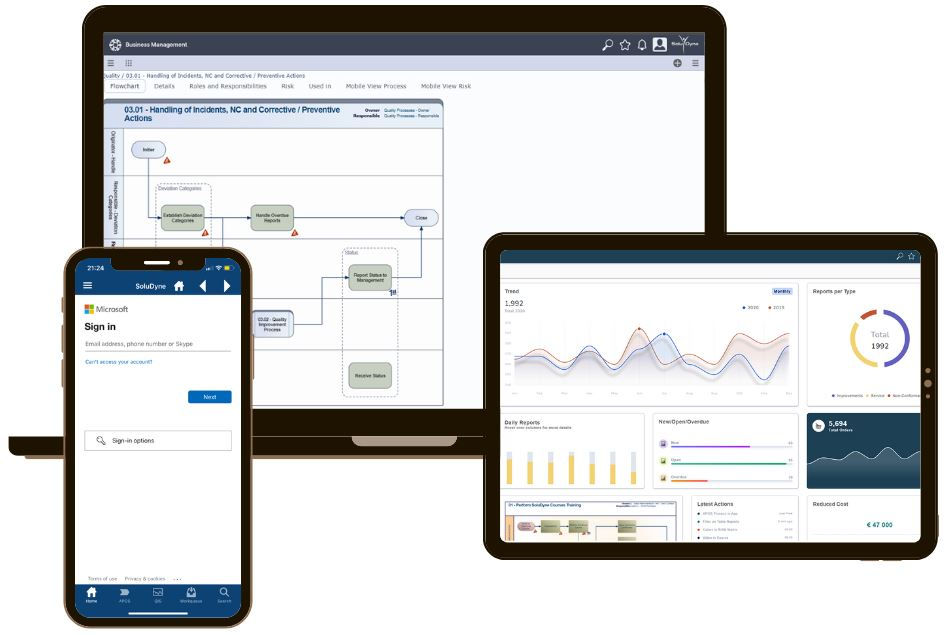

Perform reporting from anywhere!
QIS is available on mobile devices,
and supports Offline Reporting.
Create new forms and flows or modify system-included standard forms and flows.
Modify Existing or Create Forms and Work Flows.
Full Traceability
Track Changes: Full traceability on changes / entries in the forms – who has done what and when?
Dashboards
Easy to get an overview by means of user-specific dashboards with list reports and graphic KPIs.
Integrated with Action Plans and Risk
Module is seamlessly integrated with the Action Plan and Risk Management Module
Integration with other IT systems
Exhange data to or from other ERP Systems, Data Warehouse etc...
Report and get status overview from mobile device. Includes Offline Reporting Functionality.
SoluDyne Quality Improvement System Functionality
SoluDyne Quality Improvement System is a software solution that helps organizations improve their performance and efficiency. It enables users to identify, analyze, and solve problems using data-driven methods and tools. SoluDyne Quality Improvement System emphasizes that the approach to work with quality, environment and working environment must be preventive rather than corrective as it supports continuous improvement and innovation by facilitating collaboration and communication among stakeholders in compliance with ISO 9001 and ISO 10010:2022.
The system is designed to handle all types of reporting: HSE deviations, IT deviations, security deviations, quality deviations other non-conformities, observations or improvements. Examples are improvement proposals, Incidents, accidents, observations, deviations, Customer claims, applications for exemptions, audits & audit findings, SJA-Statistical Justification of Acceptance, Safety Inspection and other types HSE events and Quality findings.
Links:
What is Quality Improvement in SoluDyne?
SoluDyne QIS is the Deviation Management module in SoluDyne. The module enables organizations to manage quality improvement, to define, track and analyze KPIs, along with implementation of best practices.
The QIS system contains tools for reporting, case management, analysis with ROS and Root Cause analysis, implementation of corrective and preventive measures and verification. It includes tools for collaboration, reporting, and auditing to ensure industry-standard compliance.
The following reports is standard in the system:
Please note that while these are the types of deviations relevant to each standard, the specific requirements and expectations for managing deviations may vary based on the nature of the organization, its activities, and its industry.
Organizations implementing multiple standards might find areas of overlap where deviations can have impacts across quality, environmental, information security, and health and safety aspects of their operations.
SoluDyne Business Management Software is in compliance with ISO 9001 and it´s requirements for a Quality Management System and ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and 45001 and QHSE Management.
Continuous Quality Improvement and Incident Management in SoluDyne
WORKFLOWS
SoluDyne Workflow is a functionality that helps organizations manage their business processes and workflows. It allows users to design, create, modify, execute, monitor, and optimize workflows across different departments and systems. SoluDyne Workflow also provides features such as automation, collaboration, reporting, and analytics to improve efficiency and productivity.
The workflows in SoluDyne is based on the PDCA cycle as a simple, but powerful tool for problem-solving, quality improvement, and continuous learning. It can be applied to any process or product in any industry or domain
Continuous Improvement Process
Quality improvement is the process of identifying and implementing changes that enhance the performance and outcomes of an organization or system. Quality improvement can be applied to any aspect of an organization, such as products, services, processes, culture, or Customer satisfaction. Quality improvement methods include data collection and analysis, problem solving, benchmarking, testing, and evaluation. Quality improvement aims to achieve excellence and continuous improvement in all areas of an organization.
Quality Improvement in compliance with ISO
One of the most widely recognized and used standards for quality management systems, is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO is a network of national standards bodies that develops and publishes international standards for various fields and industries. ISO standards cover topics such as quality management, environmental management, information security, social responsibility, and more. ISO standards are voluntary, but they can help organizations demonstrate their commitment to quality and gain a competitive edge in the global market.
Quality management systems and ISO can be seen as complementary rather than contradictory. Organizations can use quality management systems to implement and improve their quality systems according to ISO standards. Alternatively, organizations can use ISO standards as a reference or benchmark for developing and evaluating their own QMS. Either way, QMS and ISO can help organizations achieve higher levels of quality and performance.
Many methods are compatible with or derived from ISO standards. For example, the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which is a common QMS tool for continuous improvement, is the core principle of ISO 9001.
Similarly, the Six Sigma methodology, which is a QMS approach for reducing defects and variation in processes, is aligned with ISO 13053, the standard for quantitative methods in process improvement.
DASHBOARDS WITH STATISTIC AND TRENDS COMPLIES WITH ISO 10010:2022
The Dashboard functionality supports guidelines and tools for collecting, analyzing, and presenting statistical data related to quality performance and Customer satisfaction according to ISO 10010:2022 guidelines.
The functionality gives an easy access to see the status of reporting via user-specific dashboards with lists and graphical
KPI´s. The Status reports and KPI has excellent overviews of reports, causes and trends that provide a basis for reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Additionally, it assists in identifying and addressing root causes of quality issues, minimizing variation and waste, and supports ISO 10010:2022 compliance, quality benchmarking, and regulatory alignment, demonstrating adherence to best practice, industry standards and customer expectations.
REPORTING IN SOLUDYNE
The system is supplied with a number of predefined reports / forms for reporting.
In this flexible solution it is possible to create new or adjust existing: reporting types, categories, forms and workflows for processing the reports.
The SoluDyne system provides possibility to report and have status overview via an internet browser or via a native app running on a handheld device.
Both secures a user-friendly reporting and provides functionality for uploading clear and factual evidence to support a report, such as documents, screenshots, recordings, and pictures/videos. This improves the collaboration between the employee and the organization and energizes the business to take initiative to report from where work is performed, as a higher focus can be on systematic quality improvement to benefit both employees and the business.
The end user can sign the report with full name, or report anonymously depending on set up of the system.
IMPROVEMENT PROPOSALS
An improvement proposal is a document that outlines a plan for enhancing an existing product, service, process, or system. It includes a concise description of the gap between the current and the desired state of a process or outcome, a cost-benefit analysis, and a timeline for implementation. Improvement proposals are used in business, engineering, education, and other fields to communicate ideas and solicit feedback from stakeholders.
The SoluDyne tool help to foster a culture of improvements aligned with ISO 9001 and ISO 10010:2022 :
The system helps out with continuous improvement as it encourage employees to report their suggestions for enhancing the quality, efficiency, or safety of their work processes. The system provides a clear and simple channel for employees to submit their suggestions and can assist in implementation, verification and monitoring the outcomes of the implemented suggestions.
The system supports the organization in implementing a system in order to align with ISO 9001 and ISO 10010:
-
Communicate the benefits of improvement suggestions for the organization and the employees, such as increased productivity, reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced employee engagement.
-
Acknowledge and appreciate every suggestion received, and provide constructive feedback on its feasibility, impact, and implementation plan.
-
Recognize and reward the employees who submit valuable suggestions, such as through public recognition, monetary incentives, or career development opportunities.
-
Share the results and lessons learned with the employees and other stakeholders
These principles are also the foundation of ISO 10010:2022, which gives guidance on the evaluation, development and improvement of organizational quality culture to help an organization to achieve sustained success. This standard is based on the quality management principles, such as customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making and relationship management.
DEVIATION REPORTING
A deviation report records any non-conformance or variation from the approved specifications, standards, or procedures for a project or a process. Reporting deviations can help prevent further incidents, protect all employees, and promote a safe and respectful work environment. The different types of deviations reports depends on the context and the purpose of the report, see examples from ISO below.
Deviation reporting according to ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 27001, and ISO 45001
These examples of ISO standards cover different aspects of quality, environmental management, information security, and occupational health and safety.
ISO 9001 - Quality
-
Audit Findings:
Audit findings are the results of an audit process that evaluates the compliance, performance, or quality of an organization, system, or process. Audit findings may identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, or risks that need to be addressed or improved. Audit findings may also provide recommendations or corrective actions to resolve any issues or problems found during the audit. Read More to learn about the Audit Program Tool. -
Change Control Deviations:
Changes to processes, procedures, or product designs without proper evaluation and authorization can lead to deviations from established quality practices. -
Customer Complaints:
Complaints from customers about product defects, delivery delays, or service issues are deviations that require investigation and resolution to ensure customer satisfaction. The reports helps to identify the root causes of customer dissatisfaction, measure the impact of customer complaints on business performance, and implement corrective actions to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty -
Documentation Errors:
Discrepancies in documentation, including incorrect specifications, incomplete records, or outdated procedures, can lead to deviations from ISO 9001 requirements. -
Non-Conformance
Non-conformance refer to instances where products, processes, or systems do not meet specified requirements. This can include deviations from quality standards, customer expectations, regulatory compliance, or internal procedures. This type of report is used to document any defects, errors, or failures in the quality of a product, service, or process. The report should include the root cause analysis, corrective actions, and preventive actions to address the deviation. -
Out-of-Specification (OOS) Results:
Deviations in test results, measurements, or analysis falling outside specified limits can lead to investigations and corrective actions to maintain quality standards. -
Product or Service Defects:
Defects in products or services can result from errors in design, manufacturing, assembly, or other processes. These deviations from expected quality standards need to be identified, investigated, and corrected. -
Process Deviations:
Deviations in processes, such as variations in process parameters, equipment malfunctions, or procedural errors, can lead to non-conformances and impact product quality. -
Supplier Non-Conformance:
When materials or components received from suppliers do not meet quality standards, it can result in deviations that need to be addressed through corrective actions.
ISO 14001 - Environmental
-
Environmental Incidents:
Deviations leading to incidents such as spills, leaks, emissions, or improper waste disposal that harm the environment. -
Non-Compliance with Environmental Regulations:
Variations from environmental laws, regulations, permits, or standards that lead to non-compliance. -
Energy and Resource Consumption Deviations:
Variations in energy usage, water consumption, or resource consumption that deviate from environmental goals. -
Environmental Aspect Deviations:
Deviations related to the identification, assessment, and management of environmental aspects, which are elements of an organization's activities, products, or services that interact with the environment.
ISO 27001 - Information Security
-
Security Incidents:
Deviations resulting in breaches of information security, unauthorized access, cyberattacks, or data leaks. -
Unauthorized Access:
Instances of unauthorized access to systems, data, or facilities, indicating security deviations. -
Data Handling Deviations:
Variations from data handling and protection procedures leading to information security risks.
ISO 45001 - Occupational Health and Safety
-
Health and Safety Accidents, Incidents and Near misses
Deviations leading to workplace injuries, illnesses, near misses, or fatalities, indicating a failure to maintain proper safety protocols. -
Unsafe Working Conditions:
Deviations in workplace conditions creating safety hazards, such as poor housekeeping or malfunctioning safety equipment. -
Non-Compliance with Health and Safety Regulations:
Variations from health and safety regulations, indicating non-compliance and potential risks to worker safety. -
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Deviations:
Instances where deviations occur in the use or provision of required personal protective equipment. -
Health and Safety Training Deviations:
Deviations related to the provision of health and safety training, such as inadequate training or failure to meet training requirements.
Support for simplified case management or full case management
The system supports simplified case management or a full case management, where the steps in the workflow are organized in relation to the PDCA cycle.
PDCA is an acronym for Plan-Do-Check-Act, which is a four-step method for continuous improvement of processes and products. It is also known as the Deming-Shewhart cycle, which is a combination of the two names to acknowledge the contributions of both Shewhart and Deming, who popularized the method in Japan after World War II.
The PDCA cycle consists of the following stages:
-
Plan: Establish objectives and processes required to deliver the desired results.
-
Do: Carry out the objectives from the previous step.
-
Check: Evaluate the data and results gathered from the do phase and compare them to the expected outcomes.
-
Act: Improve the process by identifying and eliminating the root causes of issues, inefficiencies, or non-conformities.
The system comes with different types of predefined workflows, which can easily be customized to the individual Customer needs.
Easy to create a report and start a workflow
Any new report can easily be created form the Home page of the system, or from any device such as a pad or mobile app.
How to set criticality on a report
The originator can elevate the criticality of the incident / finding when reporting, requesting that immediate supervision needs to be taken, and secure immediate action from Responsible person(s).
Example of standard steps that the system provide for a workflow, see below:
CLASSIFICATION
The case handler can set classification status, priority and decide if further action is required or not. If yes, the case handler can choose the responsible analyst to handle the case further. Alarm flag can be set in advance to notify Responsible person(s), if the same type of incident occur too often.
ANALYSIS
The analyst can perform Risk Assessment, Analyze, select Root Cause from a predefined register and document root cause directly on the report. There is functionality on each report to add Preventive and Corrective Actions to ensure task assignment and feedback to relevant employees. E-mails can be sent automatically to individual employees when they are assigned tasks.
-
Risk Assessment: The system makes it possible to perform risk assessment of an incident / QIR based on created risk matrices with probabilities, consequences and risk level. Risk Assessment and quality improvement systems are essential tools for any organization that wants to achieve its goals and objectives. Risk Assessment is the process of identifying, analyzing and evaluating the potential hazards and uncertainties that may affect the performance, quality or safety of a product, service or process.By implementing Risk Assessment and quality improvement systems, an organization can reduce the likelihood and impact of negative outcomes, increase the value and benefits of positive outcomes, and continuously monitor and improve its performance and quality standards.
-
Analysis: The analyst can review/investigate/troubleshoot the request/observation reported by the Originator and document highlights/top level information of the analysis that´s been performed. The Log functionality secures documentation while analyzing, and not only when the analysis is completed.
-
Action Plan: The Analyst can create Preventive and Corrective Actions direct on the case or look up if there are existing action which covers the case. All action can be reviewed/approved by the Case handler before hand if necessary implementation is to be performed.
-
Root Cause: The Analyst can document Root Cause in a separate comment or choose a value from the predefined Root Cause list. The root cause is the underlying factor or condition that leads to a problem or an undesirable outcome. Identifying and addressing the root cause can help prevent the problem from recurring or escalating. A common method for finding the root cause is to use the "5 Whys" technique, which involves asking "why" repeatedly until the root cause is revealed.
-
8D: A 8D report is a document that summarizes the results of an analysis of a problem or issue, the root causes, the actions taken to address it, and the lessons learned. It is often used in project management, quality improvement, and risk management. The A8 stands for the eight steps of the process: Acknowledge, Analyze, Assign, Act, Audit, Adjust, Acknowledge again, and Document. The D stands for the final step of documenting the report and sharing it with relevant stakeholders.
-
Accident Report: This analysis goes beyond the immediate cause and aims to identify underlying systemic issues, human factors, equipment failures, procedural shortcomings, or other factors that played a role in the deviation. An accident report not only documents what went wrong but also focuses on lessons learned from the incident. These lessons can inform changes to processes, procedures, training programs, equipment maintenance, and overall safety culture to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
-
Lessons Learnt: The system support for the Analyst to register Lessons Learnt using text, images and video. The system gives an overview of Lessons Learnt to the end users in a Lessons Learnt overview page.
-
SCAT: A SCAT report is a document that summarizes the results of a systematic, comprehensive and accurate assessment of a situation or a problem. A SCAT report typically includes the following sections: Situation, Causes, Actions and Targets. The purpose of a SCAT report is to provide a clear and concise overview of the current state, the root causes, the proposed solutions and the expected outcomes.
IMPLEMENTATION AND VERIFICATION
The system supports verification and implementation which are essential steps in ensuring measurable results.
Implementation of corrective or preventive actions to address the deviations, and prevent them from recurring, is required to secure continuous improvement.
Verification is needed to check and confirm that actions taken has had the intended effect. The Approver / Verification Responsible / QC can verify all cases after implementation is performed according to the PDCA cycle.

